Example of Tertiary Structure of Protein
Owing to inductive effects the basicity of an amine might be expected to increase with the number of alkyl groups. The primary structure of a protein is simply the sequence of amino acids that it is made of.
Typically taking the form of alpha helices and beta sheets.

. The degree of solvation of the protonated amine which includes steric hindrance by the groups on nitrogen. Hydrogen bonds ionic bonds and van der Waals attractions as explained in. The electronic properties of the substituents alkyl groups enhance the basicity aryl groups diminish it.
These involve atoms in the polypeptide backbone as well as atoms in the amino acid side chains. The folding of a protein chain is however further constrained by many different sets of weak noncovalent bonds that form between one part of the chain and another. Tertiary structures are even more complex forming the three-dimensional shape of the protein.
To synthesize proteins by reading codon in mRNA a tRNA molecule must have a tertiary structure. The weak bonds are of three types. The tertiary structure is the most stable structure out of all and this stability is acquired due to hydrogen bonding in between nitrogenous bases and also between nitrogenous bases and the ribose-phosphate backbone.
An example diagram of a prokaryotic organism. The basicity of amines depends on.

Protein Structure Biology Dictionary
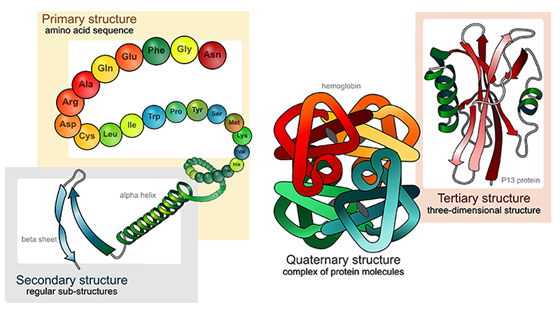
Four Types Of Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Structures

Four Types Of Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Structures
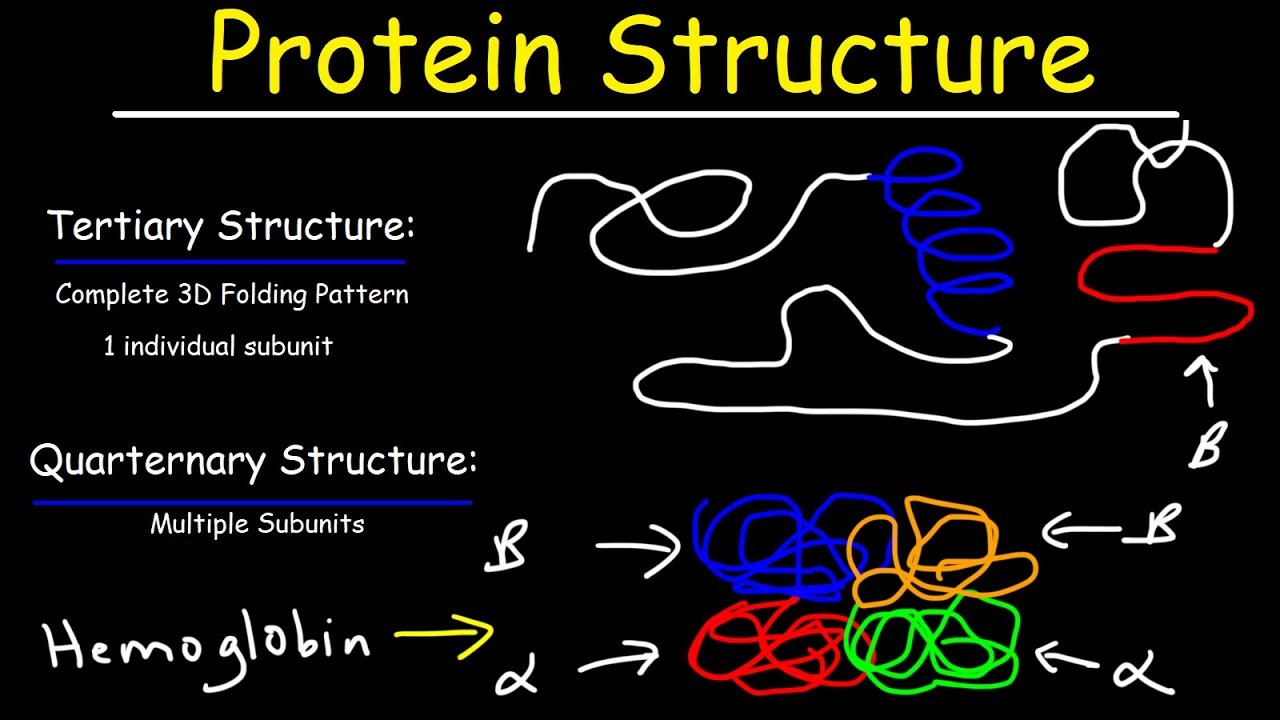
Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Biology Youtube
0 Response to "Example of Tertiary Structure of Protein"
Post a Comment